Java 插件
自动导入包,
大小写自动转换
插件ptg
变量定义
在定义
长整型(long)变量的时,需要末尾加个L(大小都可以)
long n = 999999999L
在定义
浮点型(float)变量的时,需要末尾加个F(大小都可以)
float f = 999999999F
数组
数组一旦被定义不能更改长度
int[] array = new int[]{11,22,333}; //完整形式
int[] array = {11,22,333}; //简写形式
动态创建数组
动态创建数组初始化长度,系统会默认给默认值null
String[] array =new String[15];
public class hello_world {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] array =new String[15];
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if(i<10){
array[i]= Integer.toString(i);
}
System.out.print(array[i] + " ");
}
}
}
// 打印结果: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 null null null null null
二维数组定义 遍历
public class hello_world {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr = {
{1, 2},
{3, 4}
};
for (int i = 0; i < arr[0].length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr[1].length; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + ",");
}
}
}
}
// 打印结果 1,2,3,4,
动态创建二维数组
public class hello_world {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr =new int[5][4];
System.out.println(arr[0].length+arr[1].length);
for (int i = 0; i < arr[0].length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr[1].length; j++) {
arr[i][j]=i+j;
System.out.print(arr[i][j]);
}
System.out.println("");
}
}
}
//输出结果:
//8
//0123
//1234
//2345
//3456
二维数组求【自写案例】
public class hello_world {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr = {
{1, 2, 3},
{2, 3, 4, 5},
{2, 3, 4, 5, 5},
{2, 3, 4, 5, 4, 5},
};
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int sum = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++) {
sum += arr[i][j];
}
count += sum;
System.out.print(sum + " ");
}
System.out.println("累计为:" + count);
}
}
// 输出结果:
// 6 14 19 23 累计为:62
方法重载
同一个方法名可以定义多个,但要注意一定要
区分参数个数或者返回值类型,如果相同则不构成重载关系.
public class hello_world {
public static void main(String[] args) {
sum(1, 2);
sum(2, 3, 5);
}
public static int sum(int a, int b) {
System.out.println(1);
return (a + b);
}
public static int sum(int a, int b, int c) {
System.out.println(1);
return (a + b + c);
}
}
注意:
类型顺序不同也构成重载,但是不建议使用
public class hello_world {
public static void main(String[] args) {
sum(1, 2.0);
sum(2.3, 3);
}
public static double sum(int a, double b) {
System.out.println(1);
return (a + b);
}
public static double sum(double a, int b) {
System.out.println(2);
return (a + b );
}
}
类 的定义 和引用
**定义 一个 phone 类 **
public class phone {
String name = "张三";
double price = 3333.24;
public void call() {
System.out.println("手机在打电话");
}
}
另一个模块 直接引用 上面的这个类
public class hello_world {
public static void main(String[] args) {
phone p = new phone();
System.out.println(p.name);
System.out.println(p.price);
p.call();
}
}
//输出结果:
//张三
//3333.24
//手机在打电话
构造函数【空参构造/带参构造】
创建一个构造函数
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
System.out.println("构造函数执行了哦");
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
}
引用该构造函数 创建两次实例
public class hello_world {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student stu = new Student("张三", 18);
Student stu2 = new Student();
System.out.println(stu.getName());
System.out.println(stu.getAge());
}
}
//打印结果
//构造函数执行了哦
//张三
//18
集合ArrayList的创建和增删改查
注意
增删改查都是有返回值的 需要时可以注意调用除了String类型
还有
ByteShortCharacterIntegerLongFloatDoubleBooolean
package text4;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ArrayListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("1");
list.add("2");
list.add("3");
list.add("4");
String remove = list.remove(0);
System.out.println("remove的数据为:" + remove);
String set = list.set(0, "1");
System.out.println("set被覆盖的元素为: " + set);
String st = list.get(0);
System.out.println(st + "aaa");
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println("数组的长度为: " +list.size());
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
list.set(i,10 + i+"---");
String s = list.get(i);
System.out.print(s);
}
}
}
//输出结果
//remove的数据为:1
// set被覆盖的元素为: 2
// 1aaa
// [1, 3, 4]
// 数组的长度为: 3
// 10---11---12---
停止虚拟机运行 / 退出虚拟机
System.exit(0);
快捷跳出外部循环 break [name];
在循环的前面 写一个
[name]:比如
loop:然后在最后写入
break loop;
package 学生管理系统;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class StudentSystem {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Boolean isQuit = true;
loop:
while (true) {
System.out.println("---------欢迎来到果锅学生管理系统---------");
System.out.println("1.添加学生");
System.out.println("2.退出系统");
System.out.println("请输入您的选择:");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int choose = Integer.parseInt(sc.next());
switch (choose) {
case 1: {
System.out.println("添加学生");
break;
}
case 2: {
System.out.println("退出系统");
//System.exit(0); 也可以写这个 来退出虚拟机
break loop;
}
default: {
System.out.println("没有找个选项");
break;
}
}
}
}
}
静态只能调用静态
静态方法只能调用静态方法,不能调用非静态方法和非静态变量
非静态方法可以调用所有方法和变量
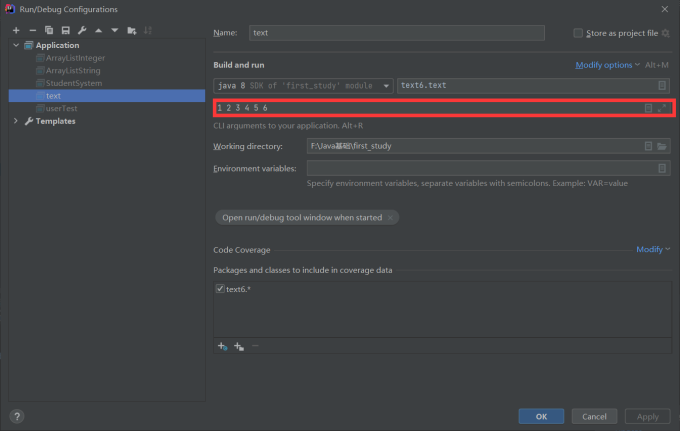
main 方法里面的 args 怎么接收参数
继承
public class Animal {
public static void eat() {
System.out.println("吃饭了");
}
public static void drink() {
System.out.println("喝水了");
}
}
public class Dog extends Animal {
public static void protectHome(){
System.out.println("看家");
}
}
public class HaShiQi_Dog extends Dog {
public static void destoryHome() {
System.out.println("拆家");
}
}
继承调用父类的变量 **super **关键字代表父类的意思
package 继承;
public class Text {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Zi z = new Zi();
z.ziShow();
}
}
class Fu {
String name = "Fu";
}
class Zi extends Fu {
String name = "zi";
public void ziShow() {
String name = "ziShow";
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(this.name);
System.out.println(super.name); //代表父类的意思
}
}
//打印结果:
// ziShow
// zi
// Fu
方法重写
Static 和 private 里面的方法不能被重写
@Override
@Override
public void eat(String dogName) {
System.out.println(dogName+"吃狗粮,吃骨头");
}
调用(带参数)构造函数
继承中构造方法的访问特点是什么?
- 子类不能继承父类的构造方法,但是可以通过super调用
- 子类构造方法的第- -行, 有一个默认的super();
- 默认先访问父类中无参的构造方法,再执行自己。
- 如果想要方法文父类有参构造,必须手动书写。
注意在
子类需要调用父类的带参数构造函数的时候需要在
子类声明同样的构造函数,并使用super关键字,进行指明构造函数**eg: **
super(name, age);
// 第一步:父类代码
public class person {
private String name;
private int age;
public person() {
System.out.println("调用了父类的构造函数");
}
public person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
System.out.println("name:" + name + ",age:" + age);
}
}
// 第二步:子类继承父类
public class student extends person {
public student() {
System.out.println("调用了子类的构造函数");
}
public student(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
}
// 第三步:实体化子类并传参
public class text {
public static void main(String[] args) {
student student = new student("张三", 16);
}
}
继承之 this 空参构造 转 有参构造
// 创建一个 person Javabean类
public class person {
String name;
int age;
String school;
public person() {
this("Guoguo", 18, "保定学院");
}
public person(String name, int age, String school) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.school = school;
System.out.println(name + "--" + age + "--" + school);
}
}
// 调用 person 实例
package a12this_空参构造;
public class text {
public static void main(String[] args) {
person person = new person();
}
}
// 输出结果
// Guoguo--18--保定学院
多态
创建多态、多态注意事项
public class text {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建对象(多态方式)
// Fu f = new Zi();
Animal a = new Dog();
// 调用成员变量;编译看左边;运行也看左边
// 编译看左边,编译的时候会看左边有没有这个变量,如果没有这个变量则会报错
// 运行也看左边,编译的时候调用的是左边的值
System.out.println(a.name); //调用父级节点里卖弄的 name 变量
// 调用成员方法
a.show(); //调用的 Dog 里面的show()方法 ,如果 Dog 里面没有这个方法,则执行父类的show()方法;
// 调用成员方法;编译看左边,运行看右边
// 编译看左边,编译的时候判断左边的父类有没有这个方法,如果有则编译成功,如果没有则编译失败
}
}
// 运行结果
// 动物
// Dog 的 show方法
判断当前子类是不是该类型 instanceof 关键字
如果
a是Dog类型 ==>if (a instanceof Dog) {...}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建对象(多态方式)
// Fu f = new Zi();
Animal a = new Dog();
if (a instanceof Dog) {
Dog b = new Dog();
b.lookHome();
} else {
System.out.println("没有这个类型");
}
}
判断类型在 JDK14 后增加了新的简便方法
if (a instanceof Dog b) {...}直接写在 类型后面先判断是不是Dog类型,如果是,则强转成Dog类型,转换之后变量名为 b
Animal a = new Dog();
if (a instanceof Dog b) {
b.lookHome();
} else {
System.out.println("没有这个类型");
}